In today’s fast-moving supply chain landscape, speed and precision are no longer optional—they’re survival tools. As e-commerce expands and customer expectations rise, companies are turning to warehouse automation to stay competitive. This transformation, powered by robotics, data analytics, and advanced logistics technology, is reshaping how goods are stored, picked, packed, and shipped around the world.
Introduction — The Race for Smarter Warehousing
Warehouses have evolved from static storage facilities into dynamic operational hubs that drive profitability and customer satisfaction. With global logistics under pressure to deliver faster and more accurately than ever before, automation has emerged as the ultimate solution. Whether through robotic systems, artificial intelligence (AI), or interconnected digital platforms, the future of warehousing lies in automation.
But the rise of warehouse automation isn’t just about efficiency—it’s also about sustainability and safety. Automated systems reduce waste, optimize energy consumption, and minimize human error, allowing companies to meet environmental goals while maintaining a competitive edge. As supply chains grow in complexity, automation acts as the invisible workforce that keeps operations running smoothly.
What Is Warehouse Automation?
Defining the Concept
At its core, warehouse automation refers to the use of digital and mechanical systems to handle repetitive or complex warehouse tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems range from barcode scanners and conveyor belts to fully autonomous robots and AI-powered management software. The goal is simple: reduce manual labor, increase accuracy, and improve operational efficiency.
Partial automation focuses on supporting workers through assistive technology—such as voice picking or automated guided vehicles (AGVs)—while full automation replaces manual processes entirely. A fully automated facility can manage inventory, direct robot movement, and process orders 24/7 with consistent precision.
The Evolution of Automated Warehouses
The journey toward automation began decades ago with mechanical handling systems and barcode tracking. However, the modern revolution took off with the integration of digital intelligence. Cloud computing, sensors, and robotics systems have transformed warehouses into connected ecosystems capable of self-monitoring and real-time optimization.
Industries like e-commerce, automotive, and manufacturing were early adopters, recognizing that data-driven automation could drastically reduce delivery times. From Amazon’s use of Kiva robots to Tesla’s AI-driven supply chain analytics, automation has become the defining feature of successful logistics operations.
The Core Technologies Behind Automation
Robotics Systems in Action
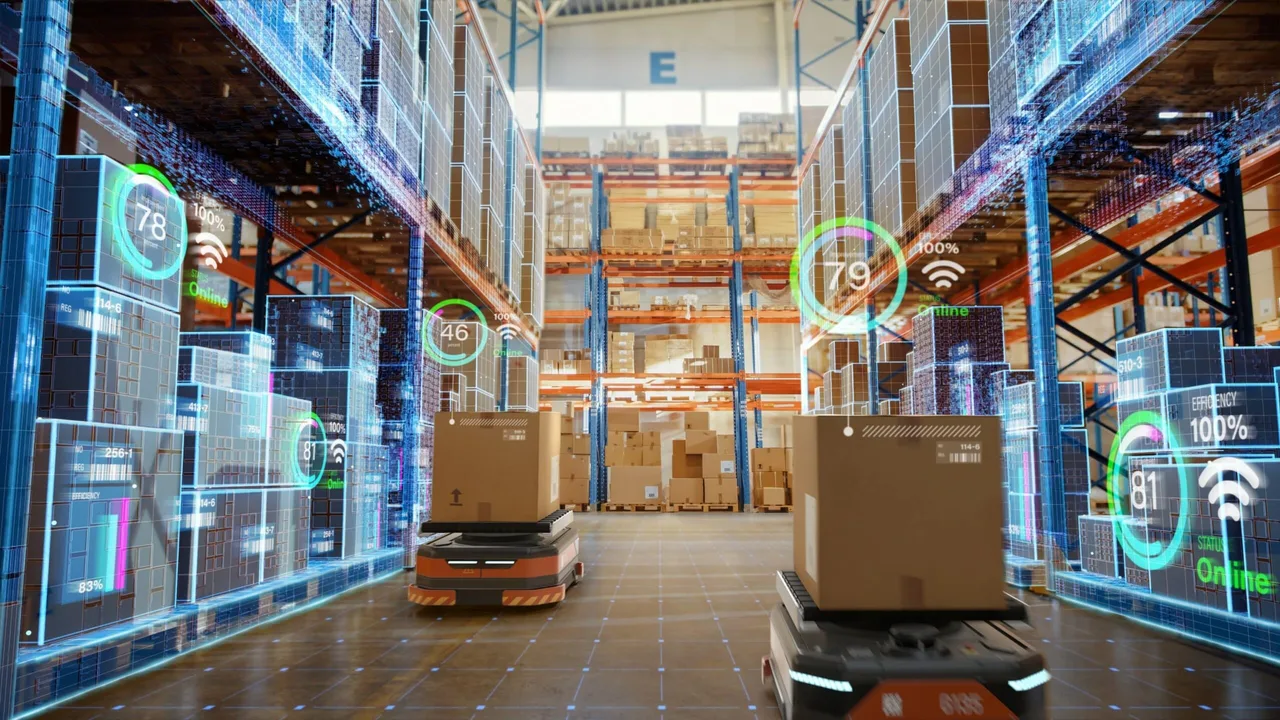
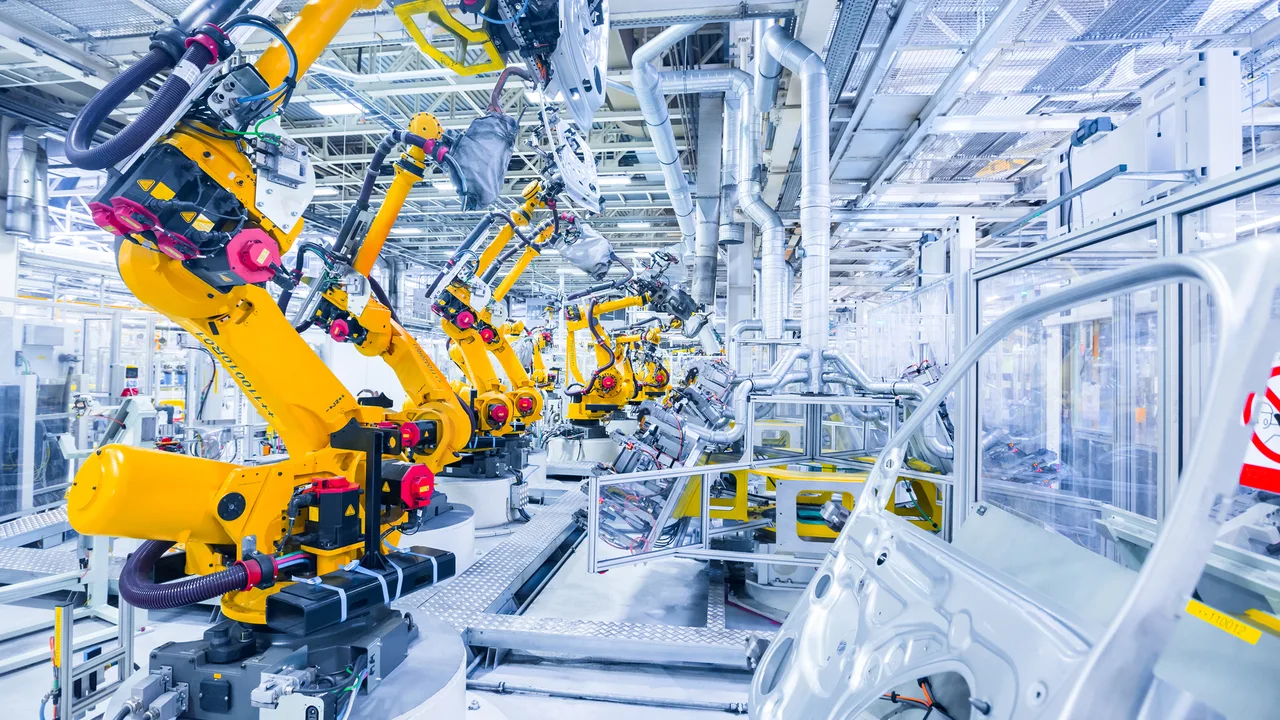
Modern warehouses rely heavily on robotic equipment to execute precise and repetitive tasks at high speed. These robotics systems range from automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that move goods across facilities to autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) capable of intelligent route planning. Robotic arms handle picking and palletizing, while drones perform real-time inventory checks from above.
Here’s how robotics are changing warehouse operations:
- Automated picking: Robots identify and collect products using computer vision, reducing error rates by over 90%.
- Sorting and packing: AI-controlled conveyors and robotic arms ensure items are correctly grouped for shipment.
- Autonomous transport: AMRs navigate through warehouse aisles, dynamically avoiding obstacles and optimizing routes.
The result is not just efficiency but also consistency—robots don’t tire, make fewer mistakes, and operate seamlessly alongside humans in hybrid work environments. This collaboration allows workers to focus on higher-value tasks like quality control and process improvement.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence amplifies the power of automation by turning raw data into actionable insights. Machine learning algorithms analyze order histories, seasonal trends, and transportation data to forecast inventory needs and optimize fulfillment routes. Predictive analytics reduce both overstocking and stockouts, ensuring that warehouses maintain the right balance between supply and demand.
AI also helps warehouses adapt in real time. For instance, if a sudden surge in orders occurs, an AI-driven system can automatically reassign robots, adjust work priorities, and reroute shipments. This agility marks a new era of responsive logistics where machines continuously learn and improve from experience.
How Automation Improves Warehouse Efficiency
Speed, Accuracy, and Cost Reduction
The greatest advantage of warehouse automation is its measurable impact on performance. Automated systems accelerate order fulfillment by streamlining workflows and minimizing manual handling. Tasks that once took hours—like order picking or inventory checks—can now be completed in minutes. The combination of speed and accuracy directly translates to reduced operational costs and higher customer satisfaction.
According to data from the Material Handling Industry, companies that integrate automated picking and data-driven logistics can boost throughput by up to 30% while cutting labor costs by nearly 25%. Moreover, automation improves scalability, allowing warehouses to handle seasonal demand spikes without the need for massive workforce expansion.
| Key Metric | Before Automation | After Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Order Accuracy | 92% | 99.7% |
| Average Fulfillment Time | 3.5 hours | 45 minutes |
| Labor Cost per Order | $2.15 | $1.20 |
Enhancing Worker Safety and Productivity
Beyond financial gains, automation greatly improves workplace safety. Repetitive and physically demanding tasks—such as heavy lifting, pallet stacking, or extended walking—can lead to injuries and fatigue. By assigning these tasks to robots, companies reduce accident rates and boost employee morale. Workers are trained to supervise machines, analyze performance data, and handle problem-solving tasks that require human judgment.
This shift doesn’t replace people; it redefines their roles. In many facilities, robots and humans collaborate through “cobots” (collaborative robots) that assist with picking and assembly, combining robotic strength with human dexterity. The result is a safer, smarter, and more engaging workplace where technology complements human potential rather than replacing it.

Integrating Warehouse Automation into Modern Supply Chains
Smart Logistics Technology
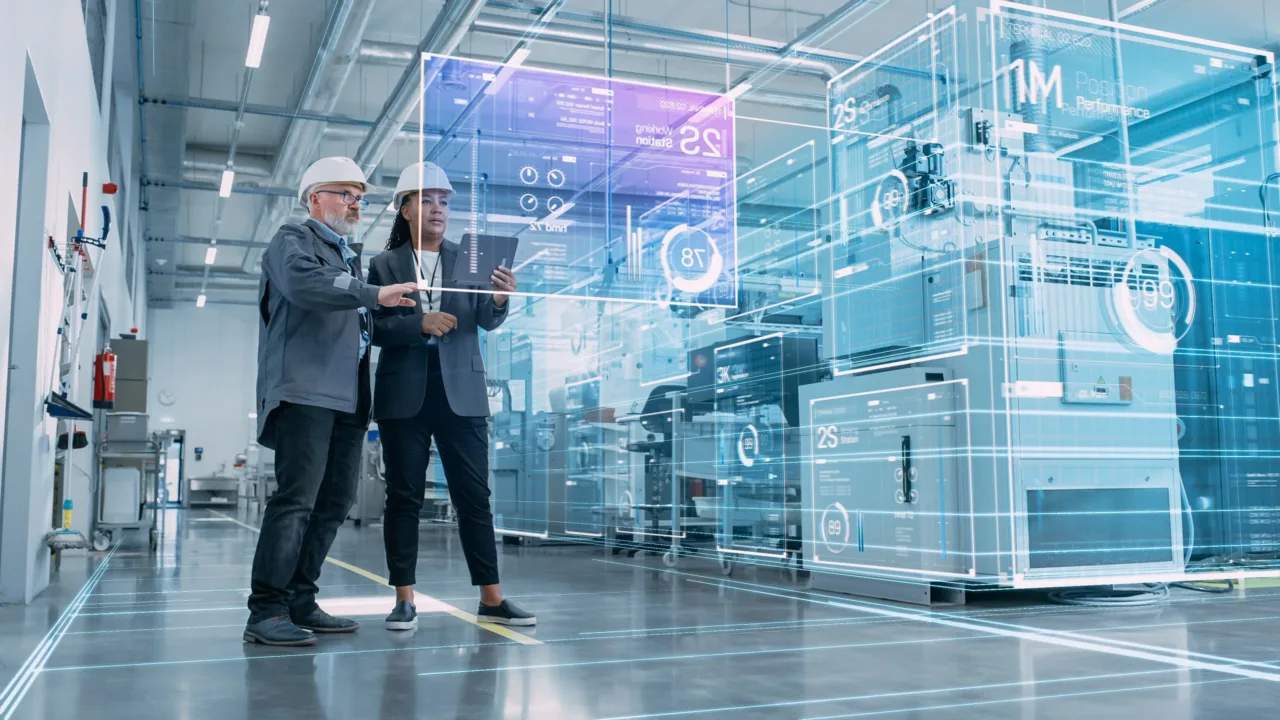
Automation doesn’t work in isolation—it thrives within a connected network. Modern supply chains use logistics technology to integrate warehouses, transportation, and retail systems into a unified ecosystem. Cloud-based management platforms allow every stakeholder, from suppliers to end customers, to access real-time data on inventory levels, delivery routes, and production status.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices embedded throughout warehouses collect and transmit data on equipment performance, temperature control, and material handling. This constant flow of information enables predictive maintenance and optimizes workflow continuity. For instance, when a conveyor motor shows signs of wear, automated alerts trigger maintenance tasks before breakdowns occur—saving both time and cost.
In addition, robotics and AI integrate seamlessly with digital twins—virtual models of physical operations that simulate and optimize warehouse performance. By testing process changes in a digital environment first, managers can make informed decisions that minimize risk and maximize efficiency in real-world operations.
Collaboration Between Systems and People
The idea that automation eliminates human jobs is outdated. Instead, the future lies in collaboration. As automation grows, so does the demand for skilled workers who can manage systems, interpret data, and ensure quality control. Human expertise remains vital for complex decision-making and exception handling that machines can’t predict.
Many companies are investing in employee upskilling programs, training workers to use data dashboards, monitor robotic systems, and troubleshoot technical issues. This hybrid environment, where humans and machines work side by side, represents the next phase of operational intelligence—one where efficiency and adaptability coexist.
The Challenges of Implementing Automation
High Initial Investment and Integration Costs
While the long-term benefits of warehouse automation are undeniable, the initial investment can be significant. Robots, AI systems, and smart sensors require capital expenditure, infrastructure adaptation, and system integration. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), this can be a major barrier to entry.
However, scalable automation solutions are emerging, allowing businesses to start small and expand as they grow. Modular systems and pay-as-you-go software models reduce upfront costs, enabling even mid-sized warehouses to automate efficiently without overextending budgets.
Data Security and System Reliability
As automation becomes increasingly connected through cloud platforms and IoT networks, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. Unauthorized access, data manipulation, or system downtime can disrupt entire supply chains. Companies must invest in encryption, multi-factor authentication, and network monitoring to safeguard their digital assets.
Reliability is equally important. Automation systems must be designed with redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms. Downtime in an automated facility can halt operations across multiple nodes, amplifying losses. Continuous monitoring, real-time alerts, and responsive maintenance strategies are essential to ensure system stability.
Future Trends in Warehouse Automation
Autonomous Logistics Networks
The next evolution of automation lies in self-managing logistics ecosystems. Through the use of AI, 5G connectivity, and autonomous vehicles, future warehouses will communicate directly with suppliers, carriers, and retailers to coordinate deliveries automatically. These systems will analyze weather conditions, traffic data, and order urgency to make real-time logistical decisions.
In this fully autonomous model, drones could handle rapid replenishment for urban distribution centers, while automated trucks deliver goods to regional hubs without human drivers. The entire process—from order placement to doorstep delivery—will be managed by interconnected digital systems that optimize themselves continuously.
Sustainability Through Smart Automation
Another transformative trend is the integration of sustainability goals within automated systems. Energy-efficient robotics, solar-powered warehouses, and waste-minimization software help companies achieve greener operations. Smart energy management systems dynamically control lighting, temperature, and machine usage to minimize electricity consumption.
These innovations align automation with environmental responsibility, allowing logistics leaders to meet ESG standards without sacrificing productivity. It’s a future where efficiency, profitability, and sustainability operate in harmony—driven by intelligent automation.
Conclusion — Building the Warehouse of the Future
The impact of warehouse automation on global logistics is profound. By combining logistics technology, AI, and robotics systems, businesses are transforming how products move from factories to consumers. Automation has proven its power not only in improving speed and precision but also in enhancing workplace safety, reducing costs, and supporting sustainable growth.
In the coming years, warehouses will continue to evolve into intelligent, adaptive ecosystems. Humans and machines will collaborate seamlessly, creating environments where innovation thrives and operations never stop. As automation continues to advance, it’s not just reshaping warehouses—it’s redefining the entire future of supply chain management.