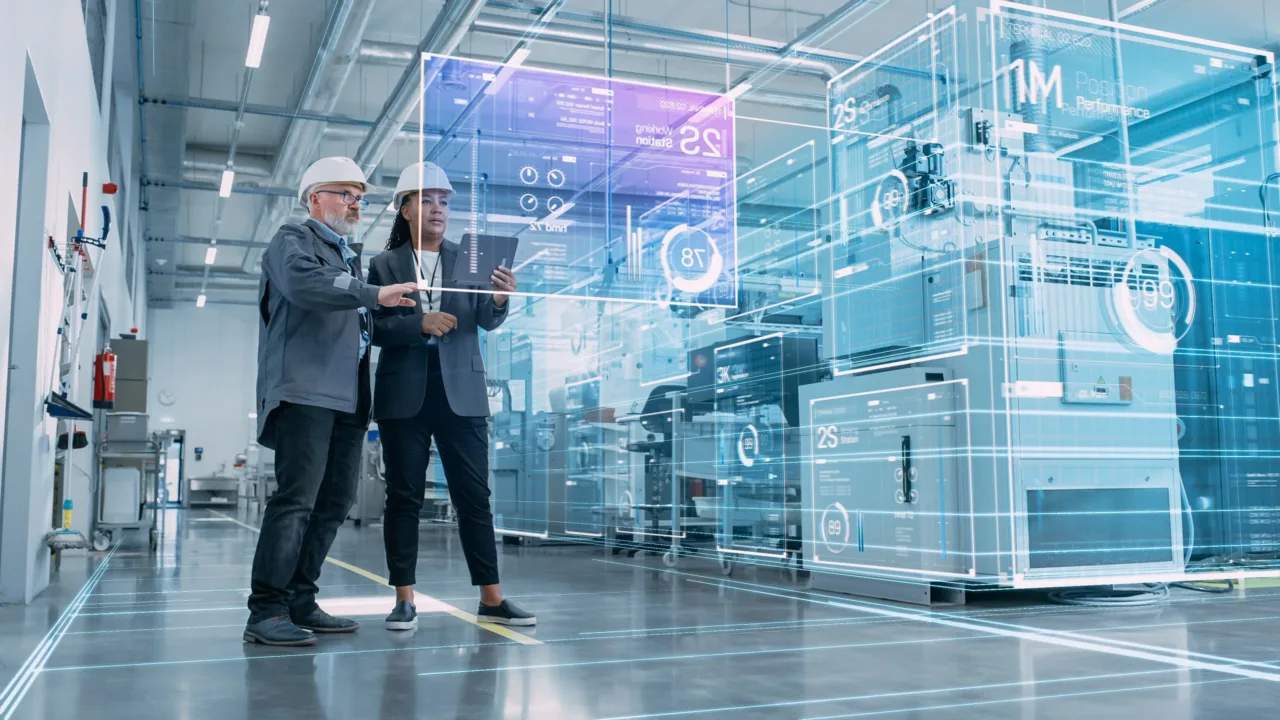
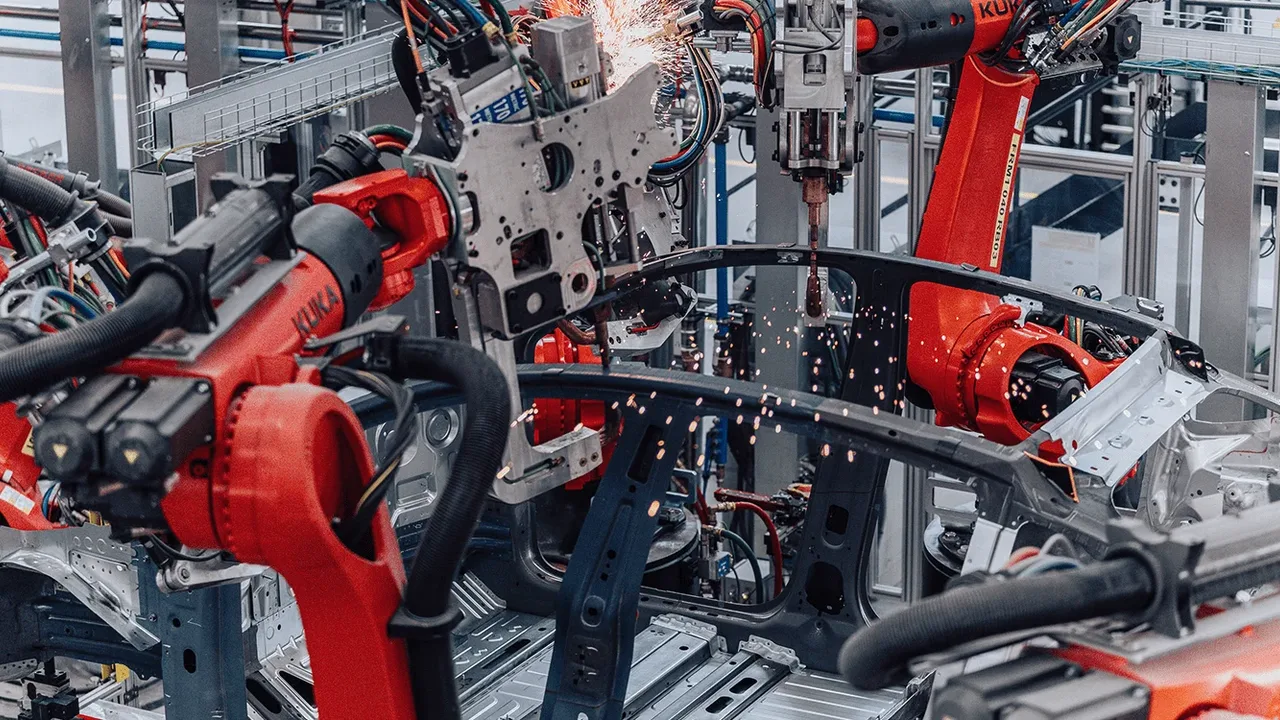
The modern industrial landscape is evolving faster than ever, and at the center of this transformation lies smart factory technology. As part of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, smart factories represent a fusion of automation, connectivity, and data-driven intelligence. These facilities are not just improving efficiency—they are redefining how production, logistics, and design operate in harmony. From intelligent robots to interconnected systems, this new wave of digital manufacturing is paving the way toward more agile and sustainable industries.
Introduction — The Fourth Industrial Revolution and the Smart Factory Boom
The world has witnessed three major industrial revolutions, each marked by innovation: mechanization, electrification, and computerization. Now, the fourth is underway—defined by connectivity and artificial intelligence. In this new era, smart factory technology enables real-time communication between machines, people, and systems. The result is a seamless network of sensors, analytics, and automation that turns data into decisions.
Whether in construction, automotive, or electronics, the concept of the smart factory is reshaping productivity standards. It offers flexibility, transparency, and sustainability that traditional production lines could never achieve. Manufacturers who embrace this shift early are positioning themselves as leaders in global competitiveness and innovation.
What Defines a Smart Factory?
From Automation to Autonomy
While automation has existed for decades, smart factories go beyond simply mechanizing tasks. They integrate industrial IoT (Internet of Things), artificial intelligence, and robotics to create autonomous environments where systems learn, adapt, and self-optimize. Machines are no longer reactive—they predict when they’ll need maintenance, adjust performance in real time, and share data with other units for better coordination.
In essence, a smart factory operates like a living organism—each machine acting as a sensory organ, feeding insights to the central nervous system: the data platform. This self-learning infrastructure drastically reduces human error while enhancing precision, productivity, and sustainability.
The Key Pillars of Smart Factory Technology
Every advanced production facility today relies on four major pillars of smart factory technology:
- Connectivity — The backbone of industrial IoT, enabling data exchange between devices, sensors, and cloud platforms.
- Automation — Use of robotics and machine vision for consistent quality and efficiency.
- Intelligence — AI algorithms that optimize manufacturing flows, detect anomalies, and improve design processes.
- Flexibility — Scalable systems that can adapt production lines to new products or demand fluctuations.
When these elements work in harmony, the factory becomes not just a production site—but an ecosystem of digital intelligence.
The Role of Industrial IoT in Digital Manufacturing
Data as the New Engine of Production
In the age of digital manufacturing, data is the most valuable resource. The industrial IoT connects machines, sensors, and operators, enabling real-time monitoring and performance tracking. For example, sensors on a CNC machine can detect temperature shifts or vibration anomalies, prompting predictive maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This proactive approach prevents costly downtime and ensures continuous operation.
Data collected across production lines feeds into analytics dashboards that provide actionable insights. Manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, predict material shortages, and fine-tune energy use—all from a centralized control system. This level of visibility is transforming not only how products are made but also how they are managed over their entire lifecycle.
Cloud Computing and Edge Integration
Smart factories thrive on fast, reliable data processing. Cloud computing offers the scalability needed to handle vast data volumes, while edge computing allows local devices to make instant decisions without relying solely on remote servers. This hybrid architecture ensures both speed and resilience.
For instance, an AI-powered inspection camera can instantly flag defects during production, while aggregated cloud data helps long-term quality improvement analysis. Together, these technologies enhance every level of smart factory technology—from equipment performance to executive strategy.
Smart Factory Technology in Action
AI and Machine Learning for Process Optimization
Artificial intelligence plays a critical role in transforming raw data into actionable improvements. Machine learning algorithms analyze production trends, detect inefficiencies, and recommend optimizations. For example, if a robotic arm shows inconsistent welding patterns, the AI system adjusts speed and pressure parameters automatically. This ensures consistent quality without halting the line.
According to research from McKinsey & Company, companies implementing AI in their production environments report up to 30% gains in operational efficiency. This synergy between analytics and automation marks the beginning of a new manufacturing paradigm—one where machines continuously evolve alongside human expertise.
Robotics and Automation
Smart factories rely heavily on robotic systems that handle repetitive, high-precision, or hazardous tasks. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) move materials across production floors, while collaborative robots—or “cobots”—work safely beside humans, boosting both safety and speed. These systems eliminate downtime caused by fatigue or human error while freeing workers to focus on supervision and innovation.
In industries like automotive or steel manufacturing, this integration has accelerated output and improved product reliability. Robots don’t just replace human labor—they enhance it, ensuring that every stage of digital manufacturing achieves new levels of excellence.
The Infrastructure Behind Smart Factories
Building Smart Factories with Modern Engineering
A truly intelligent production environment requires equally advanced physical infrastructure. The structural design of the facility must support high-tech installations, automation systems, and heavy machinery layouts. Here, modern steel engineering plays a key role. A leading steel structure company in china has demonstrated how modular design and precision fabrication can accelerate smart factory construction while maintaining flexibility for future technological upgrades.
Steel structures not only allow faster assembly but also provide superior adaptability. They can easily accommodate additional production lines, expanded data centers, or enhanced ventilation systems needed for AI-powered machinery. This combination of digital and structural innovation lies at the heart of the smart factory movement.

Benefits of Smart Factory Implementation
Efficiency, Accuracy, and Sustainability
Companies adopting smart factory technology are reporting groundbreaking results. Automated processes ensure precision that manual operations could never achieve, reducing human error and increasing consistency. With real-time monitoring and machine-to-machine communication, production systems can adapt instantly to fluctuations in demand or raw material availability. This flexibility minimizes waste and maximizes output.
Energy efficiency is another significant advantage. Through industrial IoT integration, sensors continuously monitor power consumption and identify areas for optimization. Machines can automatically enter low-energy modes during downtime, cutting operational costs without affecting productivity. These same systems also track material use and emissions, helping companies align with global sustainability goals and reduce carbon footprints.
- 20–30% improvement in production efficiency after full digital adoption.
- 15% reduction in material waste due to predictive resource management.
- 25% faster turnaround through automated scheduling and workflow synchronization.
For manufacturers, these numbers represent more than performance—they symbolize long-term resilience and competitive advantage in a fast-changing market.
Business Competitiveness and Scalability
As global industries accelerate their digital transformation, scalability has become a defining factor of success. With digital manufacturing, factories can rapidly expand production capacity without building entirely new facilities. New machines, sensors, or robotic arms can be added seamlessly to the existing digital ecosystem.
Moreover, the insights generated by AI help companies make smarter decisions about investments and product design. From forecasting demand to optimizing supply chain logistics, smart factory technology ensures that every process is informed by data, not guesswork. The result: more agile business models capable of adapting to global economic shifts.
The Global Landscape of Smart Manufacturing
Asia’s Leading Role in Industrial Transformation
Asia has become the driving force behind the world’s smart factory movement. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have invested heavily in industrial IoT and AI-driven production systems. Supported by government initiatives and partnerships between technology providers and manufacturers, these nations are setting new global standards in efficiency and scale.
For example, large industrial parks in China now host hundreds of interconnected facilities where machines, logistics systems, and enterprise software operate under one digital network. These hubs illustrate how the combination of digital manufacturing and industrial policy can accelerate nationwide modernization.
Western Innovation Meets Eastern Scale
While Asia leads in deployment, Europe and North America focus on innovation and sustainability. Companies in Germany and the U.S. are developing advanced robotics, cybersecurity frameworks, and energy-efficient automation systems. Collaboration between Eastern manufacturing power and Western technological research is shaping the next phase of industrial growth—where smart factories will operate across continents with unified digital standards.
This global integration is expected to give rise to hybrid production networks where factories share data in real time to balance workloads, manage inventory, and reduce emissions. It’s a vision of global manufacturing that’s not only efficient but also environmentally responsible.
Challenges and the Path Ahead
Technical Barriers and Workforce Gaps
Despite its promise, adopting smart factory technology isn’t without obstacles. The initial cost of upgrading legacy systems and training staff can be substantial. Many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) struggle with the complexity of integrating new digital infrastructure into traditional workflows. Additionally, the demand for skilled workers in data science, AI, and automation continues to outpace supply.
Governments and educational institutions are now stepping in, introducing vocational programs focused on digital manufacturing and robotics engineering. The goal is to close the talent gap and make smart factory adoption accessible beyond large corporations. As this talent pool expands, so will the global pace of industrial transformation.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
With increasing connectivity comes increased risk. As machines, sensors, and cloud platforms share data, companies must guard against cyber threats and data breaches. Implementing AI-based security systems and blockchain-based traceability can mitigate these challenges, ensuring that production remains both safe and transparent. The integration of cybersecurity protocols within industrial IoT architecture has become a non-negotiable requirement for all smart factory operators.
The Future of Smart Factories
Looking forward, smart factories will evolve into fully autonomous ecosystems. AI systems will manage production lines, supply chains, and even procurement automatically. Predictive algorithms will coordinate global logistics, while digital twins—virtual replicas of physical factories—will simulate operations in real time to optimize efficiency.
In the next decade, expect factories that run on renewable energy, powered by AI that adjusts workloads based on carbon intensity. These innovations will mark a turning point in how industries approach both profitability and environmental responsibility. The promise of smart factory technology is clear: to build a world where intelligence and sustainability coexist.
The Smart Factory Revolution is Here
The rise of smart factory technology is redefining industrial progress. Fueled by industrial IoT, robotics, and digital manufacturing, factories are becoming more autonomous, efficient, and sustainable than ever before. From real-time analytics to self-learning systems, the synergy of data and automation is reshaping how goods are produced and delivered across the globe.
This transformation isn’t just about technology—it’s about people, innovation, and vision. Industries that embrace this digital shift are not only future-proofing their operations but also contributing to a smarter, greener planet. The smart factory revolution is no longer a concept; it’s the foundation of tomorrow’s global economy.