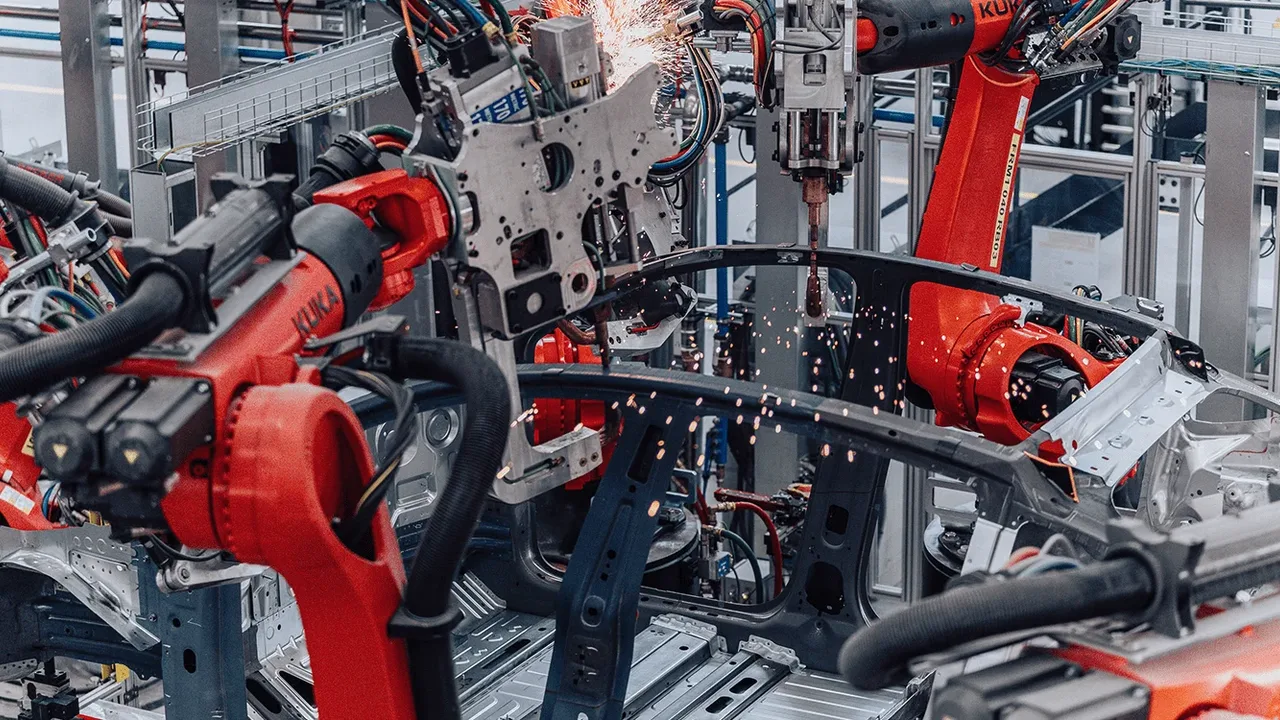
As the world faces rising construction demands and labor shortages, robotics construction has emerged as a revolutionary solution. From autonomous machinery and robotic arms to large-scale 3D printing systems, automation is redefining how buildings are designed and executed. What was once considered futuristic is now becoming an integral part of global infrastructure development, blending innovation with practicality.
A New Era of Automated Construction
Construction has traditionally relied on human skill, physical endurance, and manual coordination. Yet as project complexity increases, so does the need for precision, speed, and safety. Enter robotics—a force that bridges digital intelligence with mechanical efficiency. Today’s robots don’t just perform repetitive tasks; they analyze, adapt, and collaborate with human workers.
This new wave of robotics construction merges disciplines like artificial intelligence, 3D printing, and smart building technologies. Together, they form the foundation for what many call “Construction 4.0”—a movement focused on digital transformation, automation, and sustainability. Around the world, construction robots are welding, laying bricks, assembling steel frames, and even printing entire houses with remarkable accuracy.
The Evolution of Robotics in Construction
From Manual Labor to Machine Collaboration
The concept of automation in construction isn’t entirely new. The earliest examples appeared in the late 20th century when Japan experimented with robotic systems to address aging workforces. Back then, these machines were limited to repetitive, predefined motions. Today’s robots, however, can sense their surroundings, interpret data, and make real-time decisions—essentially becoming collaborative partners on site.
What makes this era different is the integration of robotics with cloud computing, sensors, and AI algorithms. Machines now perform with human-like dexterity while maintaining accuracy levels no human could sustain for long periods.
The Role of Digital Transformation
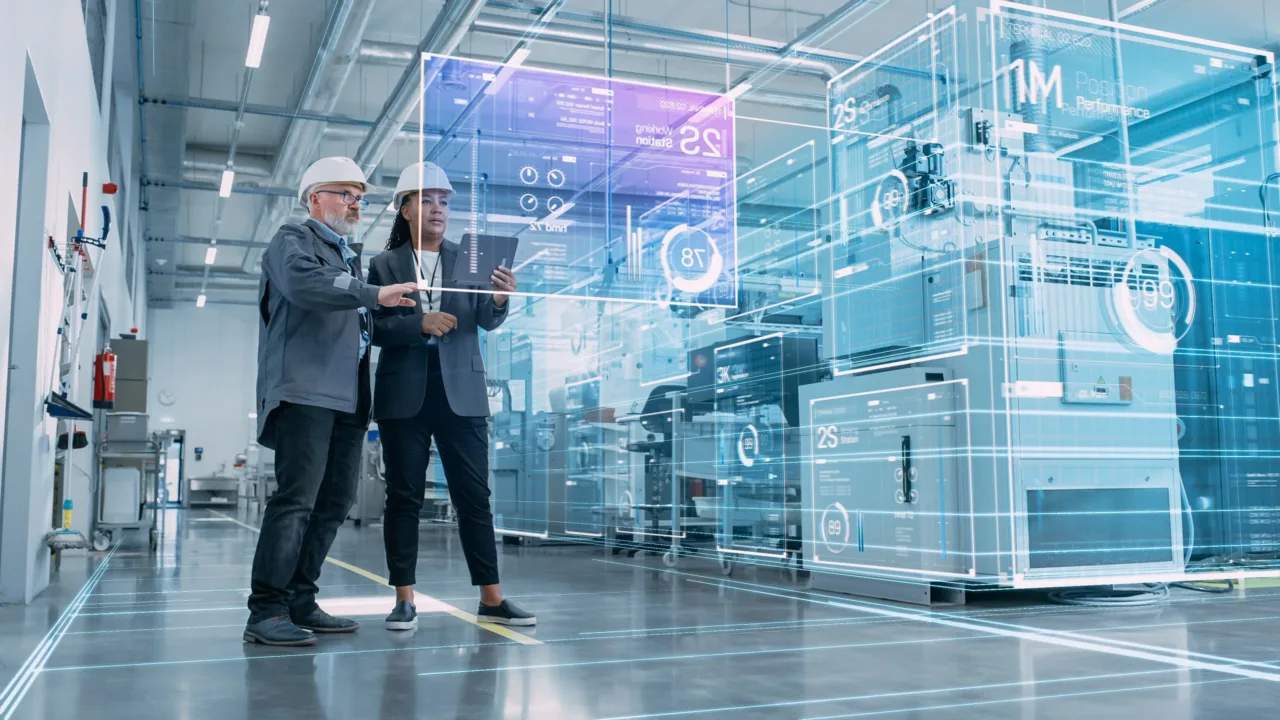
Digital transformation is the invisible backbone of modern construction automation. Building Information Modeling (BIM) allows engineers and architects to create digital twins of entire projects, enabling robots to follow precise geometric data. Combined with real-time sensors and data analytics, BIM helps synchronize every robotic movement—from material delivery to structural assembly.
In other words, robotics construction is not just about physical machines—it’s about a connected digital ecosystem that merges hardware, software, and human expertise to achieve flawless coordination.
Core Technologies Powering Robotics Construction
Industrial Robots and Autonomous Machines
One of the most visible aspects of construction automation is the deployment of heavy-duty robots and self-driving machinery. Autonomous excavators, drones for surveying, and robotic bricklayers are now common sights on innovative project sites. These systems can operate around the clock, unaffected by fatigue or environmental conditions, significantly boosting productivity.
- Autonomous Excavation: GPS-guided excavators dig with centimeter-level precision.
- Robotic Welding and Assembly: Automated welders ensure consistent joint strength and safety.
- Survey Drones: Aerial mapping reduces human risk while accelerating data collection.
These technologies reduce accidents, improve quality control, and help developers complete projects faster—without sacrificing accuracy.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
Perhaps the most exciting frontier in construction is 3D printing. Additive manufacturing uses automated robotic arms to layer concrete, steel, or composite materials, creating structures faster and with less waste than traditional methods. From emergency housing units to bridges and public installations, 3D printing is rewriting how we think about building.
Projects in Dubai and the Netherlands have already demonstrated that 3D-printed construction can cut costs by up to 60% while reducing waste materials by half. The combination of robotic precision and digital design freedom enables architects to create complex geometries previously deemed impossible.
Smart Building Systems and AI Integration
Internet of Things (IoT) and Real-Time Coordination
Modern construction sites are evolving into interconnected networks of intelligent machines. IoT sensors placed on equipment and materials continuously feed data into centralized systems. This allows real-time monitoring of structural integrity, temperature, humidity, and energy use. Through such data, robots and human supervisors coordinate operations with unprecedented accuracy.
For example, a crane equipped with IoT sensors can automatically adjust its operation based on wind speed, while autonomous vehicles navigate construction zones using dynamic route optimization. This interconnectivity embodies the concept of a smart building—one that begins learning even before it’s completed.
Predictive Maintenance and Self-Learning Robots
Beyond construction, artificial intelligence is transforming how robots maintain themselves. Predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data to forecast mechanical wear and tear before failure occurs. Self-learning robots use this data to improve task performance, reducing downtime and maximizing uptime on site.
For developers, this means fewer interruptions, lower maintenance costs, and greater reliability. It’s a future where buildings are not just constructed by intelligent machines—but maintained by them as well.

Case Studies — Global Innovations in Robotics Construction
Around the world, construction sites are transforming into laboratories of innovation. In Japan, autonomous robots are laying rebar, pouring concrete, and inspecting work for precision, compensating for an aging workforce. In the United States and the United Arab Emirates, companies are scaling up robotics construction through entire 3D-printed neighborhoods. These projects demonstrate that automation is not just possible—it’s practical, efficient, and scalable.
Europe has taken a slightly different path, focusing on smart collaboration between machines and workers. Autonomous drones map urban zones while robotic arms execute high-precision assembly under human supervision. Each example illustrates how automation adapts to local labor conditions and cultural expectations while maintaining universal goals: speed, safety, and sustainability.
Benefits of Robotics in Construction
Precision and Speed
Robots bring unmatched accuracy to construction. Tasks such as welding, drilling, or material handling that once took hours can now be completed in minutes. Robots don’t tire or make judgment errors, which minimizes human risk and eliminates costly rework. Advanced algorithms allow these systems to continuously refine their techniques, achieving consistent results across hundreds of repetitive tasks.
Safety and Labor Efficiency
Safety is one of the biggest advantages of automation. Construction remains one of the world’s most dangerous industries, but robots can handle hazardous environments—from high scaffolds to confined underground tunnels. This shift allows human workers to focus on design, quality control, and innovation rather than physically risky operations.
- Reduced Workplace Accidents: Robots take over dangerous manual tasks.
- Higher Workforce Productivity: Humans supervise, strategize, and innovate.
- Continuous Operations: Machines can work 24/7 under supervision without fatigue.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
One of the lesser-known benefits of robotics construction is its contribution to sustainability. Robotic systems optimize material use and reduce waste through precision cutting and layering. When integrated with 3D printing and data analytics, these systems create structures using exactly the amount of material needed—no more, no less. This efficiency directly supports green building initiatives and the broader goals of sustainable urbanization.
Challenges and Limitations
High Initial Costs and Skill Gaps
Despite the promise of automation, barriers to adoption remain significant. The upfront cost of robotic equipment, software integration, and workforce training can deter smaller firms. Many construction workers also lack exposure to programming or robotic maintenance, making the learning curve steep. Bridging this skill gap is critical to ensuring equitable access to automation across the industry.
Integration and Standardization
The next challenge lies in creating interoperable systems. Different regions use varied software standards and communication protocols, making it difficult to integrate robots from multiple suppliers. Furthermore, some architects worry that over-reliance on automation might limit design creativity. Achieving balance between precision and artistic expression will be key as the industry evolves.
The Future Outlook of Robotics Construction
Toward Fully Automated Building Sites
The vision for the next decade is clear: fully automated construction sites operating with minimal human intervention. As AI, drones, and 3D printing continue to merge, entire structures will be assembled through self-organizing workflows. Robots will coordinate in real time, exchanging data through digital twins and cloud-based monitoring systems.
Imagine a project where autonomous vehicles deliver materials, robotic cranes perform assembly, and drones oversee progress—all managed by AI-driven analytics dashboards. This is not science fiction; pilot programs in Asia and Europe are already testing this model. The result: faster timelines, improved accuracy, and greater sustainability across the construction lifecycle.
The Role of Human Supervision and Ethics
Even in a highly automated future, humans remain indispensable. Machines can execute instructions, but ethical decision-making, creative design, and contextual judgment belong to people. The integration of robotics raises new questions about job displacement and technological responsibility. To move forward responsibly, industries must ensure that human expertise remains central to every digital innovation.
Building the Future, One Robot at a Time
The rise of robotics construction marks a transformative moment for the built environment. From large-scale 3D printing to AI-assisted smart building systems, automation is solving many of the industry’s toughest challenges—speed, safety, and sustainability. Yet the ultimate success of this transformation depends on human leadership: visionaries who understand how to merge technology with purpose.
By embracing robotics as a partner rather than a replacement, the construction sector can build smarter, faster, and greener than ever before. The future isn’t about choosing between people and machines—it’s about designing a world where they build together.