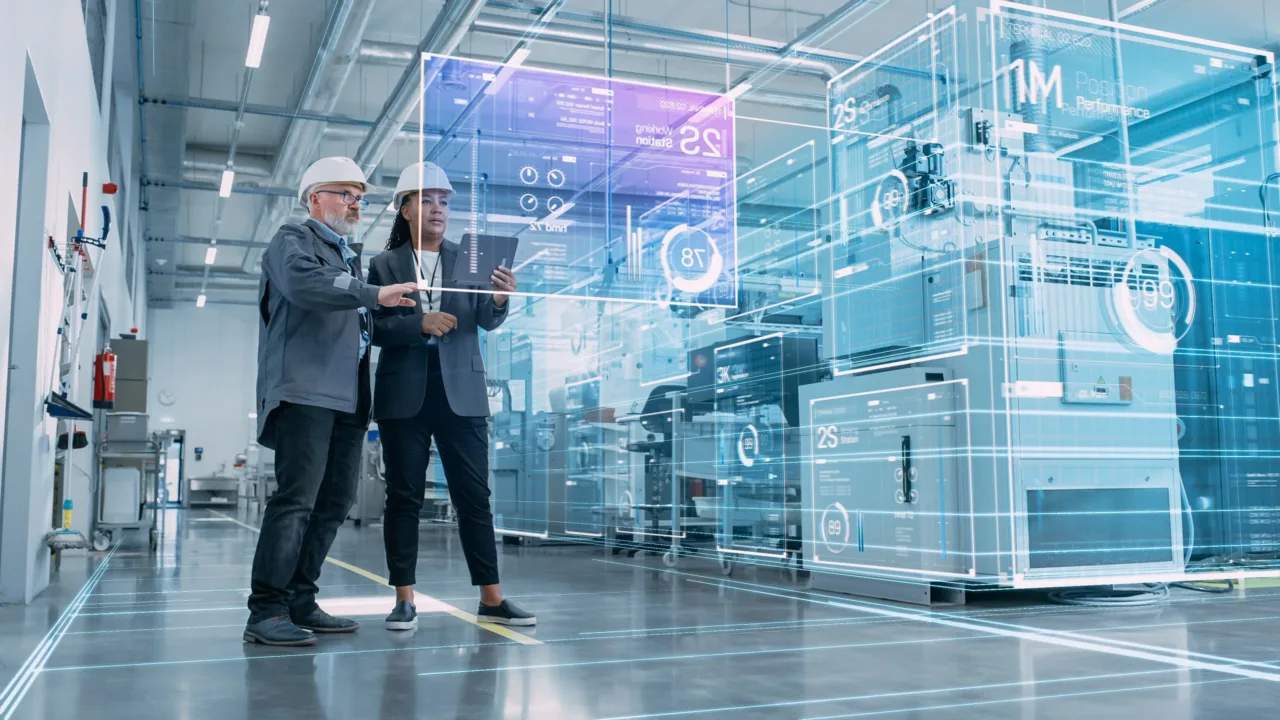
The manufacturing sector is undergoing one of the most significant transformations in its history. What was once driven by manual reporting, intuition, and fragmented spreadsheets is now powered by big data manufacturing systems that process millions of data points in real time. In today’s competitive landscape, companies that rely on data-driven insights consistently outperform those that depend solely on experience or legacy processes.
From predictive maintenance to intelligent scheduling, data analytics has become the backbone of modern factories. The ability to collect, analyze, and act on massive datasets enables manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of production optimization. In this new industrial era, data is not just a support tool—it is a strategic asset.
Introduction — The Data Revolution in Modern Manufacturing
The fourth industrial revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0, has redefined how factories operate. Connected machines, IoT sensors, and cloud platforms continuously generate streams of operational information. This environment has created the perfect foundation for big data manufacturing to thrive.
Instead of reacting to issues after they occur, manufacturers now use predictive models to anticipate problems before they disrupt production. Instead of relying on static schedules, they dynamically adjust workflows based on live metrics. This shift represents more than a technological upgrade—it marks a cultural transformation toward evidence-based decision-making.
Understanding Big Data in Manufacturing
What Is Big Data Manufacturing?
Big data manufacturing refers to the integration of massive datasets into industrial operations to improve efficiency, quality, and cost control. Unlike traditional reporting systems that analyze historical data, modern platforms process information in real time.
Big data in manufacturing typically includes:
- Machine performance data from sensors
- Production cycle times
- Quality inspection results
- Supply chain logistics metrics
- Energy consumption statistics
These datasets are characterized by what experts call the “three Vs” of big data:
| Characteristic | Description | Manufacturing Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | Massive amounts of machine-generated data | Enables comprehensive process visibility |
| Velocity | Real-time data generation and processing | Supports instant decision-making |
| Variety | Multiple data formats (structured & unstructured) | Improves cross-functional integration |
By combining these elements, data analytics platforms transform raw machine outputs into actionable insights.
The Role of Data Analytics in Industrial Systems
Without advanced data analytics, big data would simply remain a collection of numbers. Analytics tools use algorithms, statistical modeling, and machine learning to uncover patterns that humans might miss.
For example, vibration sensors on a production line can detect subtle anomalies that indicate future mechanical failure. By analyzing historical data trends, predictive models can estimate when a component is likely to fail. This capability allows maintenance teams to intervene proactively, reducing downtime and avoiding costly disruptions.
According to insights published by McKinsey & Company, data-driven manufacturing operations can increase productivity by up to 30% when analytics is properly integrated into decision-making processes. This demonstrates how powerful structured information can be when embedded into daily workflows.
How Big Data Improves Production Optimization
Predictive Maintenance and Downtime Reduction
One of the most impactful applications of big data manufacturing is predictive maintenance. Traditional maintenance schedules rely on fixed intervals, which can either be too early—wasting resources—or too late—causing breakdowns.
With real-time monitoring and data analytics, factories can predict equipment failures before they happen. Sensors track temperature, vibration, and load conditions continuously. Algorithms compare live readings with historical performance to detect early warning signs.
The benefits include:
- Reduced unexpected downtime
- Lower repair costs
- Extended equipment lifespan
- Improved safety standards
This shift directly contributes to production optimization, ensuring that machinery operates at peak efficiency without unnecessary interruptions.
Smart Scheduling and Resource Allocation
Another area where big data manufacturing excels is scheduling. Traditional production planning often relies on static forecasts. However, real-world manufacturing conditions constantly change—supplier delays, machine maintenance, or fluctuating demand can disrupt even the best-laid plans.
Advanced data analytics systems continuously evaluate variables such as order priority, machine capacity, workforce availability, and energy usage. This allows managers to dynamically reallocate resources in response to real-time changes.
Through intelligent scheduling, factories achieve:
- Shorter lead times
- Better workforce utilization
- Reduced material waste
- Higher overall output consistency
These improvements form the backbone of modern production optimization strategies, where efficiency is measured not just by speed, but by adaptability and precision.
Real-Time Decision Making with Data Analytics
Monitoring Performance Metrics
In highly competitive markets, operational visibility determines survival. Modern dashboards powered by big data manufacturing platforms provide managers with instant access to key performance indicators (KPIs) such as throughput rate, defect percentage, and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
Rather than waiting for end-of-week reports, supervisors can identify inefficiencies within minutes. This real-time insight allows for immediate corrective action, minimizing losses and stabilizing output.
The transition from reactive management to proactive oversight represents one of the greatest advantages of data analytics. Instead of responding to problems after financial damage occurs, manufacturers prevent them from escalating in the first place.
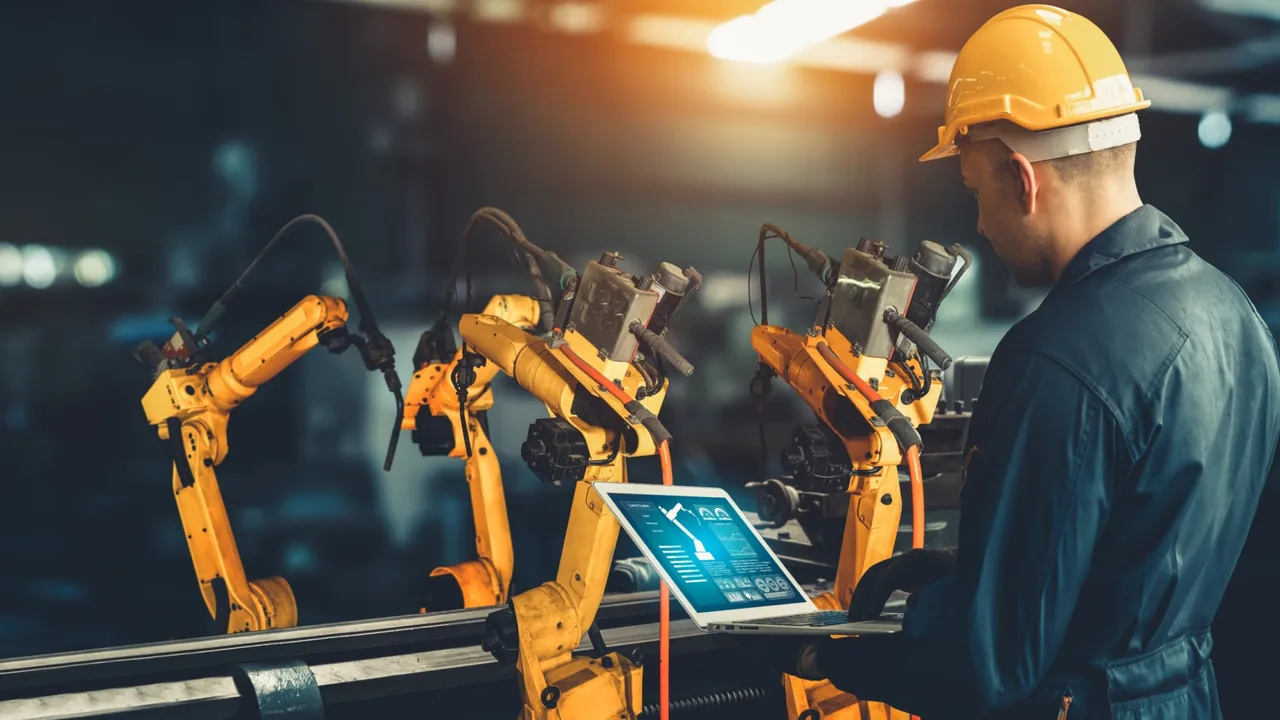

The Competitive Advantage of Big Data Manufacturing
Cost Efficiency and Waste Reduction
One of the strongest arguments for adopting big data manufacturing lies in its direct financial impact. Manufacturing margins are often tight, and even minor inefficiencies can accumulate into significant losses. By leveraging data analytics, companies gain visibility into hidden waste—whether in raw material usage, energy consumption, or idle machine time.
For instance, data collected from production lines can reveal micro-stoppages that would otherwise go unnoticed. Over time, these small interruptions add up. With proper analysis, managers can identify bottlenecks and implement targeted improvements that drive production optimization.
Material efficiency also improves dramatically. Advanced modeling systems calculate optimal cutting patterns, resource allocation, and batch processing sequences. This reduces scrap rates and ensures that every unit of material contributes maximum value. In industries where raw materials represent a large portion of costs, this alone justifies investment in big data manufacturing systems.
Enhancing Product Quality
Quality control is no longer limited to end-of-line inspection. Modern data analytics tools monitor product parameters throughout the manufacturing cycle. By analyzing temperature, pressure, timing, and calibration metrics in real time, factories can detect deviations before they result in defective output.
Pattern recognition algorithms identify recurring defect sources, enabling permanent corrective measures rather than temporary fixes. This proactive quality management strengthens brand reputation and reduces costly recalls.
Through consistent monitoring and feedback loops, production optimization becomes a continuous process rather than a one-time initiative. Quality, speed, and cost efficiency move in alignment instead of competing against each other.
Challenges in Implementing Big Data Manufacturing
Infrastructure and Investment Barriers
Despite its benefits, implementing big data manufacturing requires substantial upfront investment. Companies must upgrade legacy systems, install IoT sensors, integrate cloud platforms, and train personnel in advanced data analytics tools. Smaller manufacturers may struggle with capital allocation, especially if returns are not immediate.
Integration complexity presents another challenge. Many factories operate on decades-old software that does not easily communicate with modern platforms. Bridging this technological gap requires careful planning and phased implementation strategies.
Data Security and Workforce Adaptation
As manufacturing systems become more connected, cybersecurity risks increase. Protecting proprietary designs, operational data, and supply chain information becomes a top priority. A robust cybersecurity framework is essential to safeguard the integrity of big data manufacturing systems.
Workforce adaptation is equally critical. Operators, engineers, and managers must learn how to interpret dashboards, manage automated systems, and collaborate with AI-driven tools. Upskilling employees ensures that data analytics insights translate into meaningful operational improvements.
The Future of Big Data Manufacturing
AI Integration and Autonomous Factories
The next phase of big data manufacturing involves deeper AI integration. As machine learning algorithms mature, factories will move closer to autonomous operations. Intelligent systems will adjust production parameters automatically, balancing speed, cost, and quality without waiting for human approval.
In these environments, production optimization becomes dynamic and self-correcting. Machines will communicate across production lines, predicting demand shifts and adjusting workflows accordingly. This level of coordination reduces delays and maximizes throughput.
Sustainable and Intelligent Production Systems
Sustainability is increasingly tied to data transparency. Advanced data analytics platforms can track carbon emissions, energy usage, and resource consumption across every stage of manufacturing. This supports compliance with environmental regulations while improving operational accountability.
By aligning sustainability goals with measurable performance metrics, big data manufacturing enables responsible growth. Companies can demonstrate reduced waste, optimized energy use, and improved lifecycle efficiency without sacrificing profitability.
From Reactive to Strategic Manufacturing Leadership
The shift toward big data manufacturing represents more than technological adoption—it signifies strategic transformation. Leaders no longer rely on intuition alone; instead, they combine experience with actionable insights derived from data analytics.
Factories that once operated reactively now anticipate market changes, equipment needs, and quality challenges. This foresight strengthens resilience, particularly in volatile global supply chains. As competition intensifies, production optimization becomes a defining characteristic of high-performing enterprises.
Building Smarter Factories Through Data
The evolution of manufacturing is inseparable from data. Big data manufacturing empowers companies to make informed, precise, and forward-looking decisions. By integrating data analytics into every operational layer, manufacturers achieve measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
As industries continue to digitalize, those who embrace intelligent systems will lead the next wave of innovation. Through continuous production optimization, manufacturers can transform factories into agile, competitive, and future-ready ecosystems driven by insight rather than guesswork.