As industries evolve toward smarter, more connected systems, robotics in workplace innovation is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s happening now. From manufacturing floors to office environments, robots are transforming the way we work, creating a new balance between human skill and technological precision. This transformation, powered by industrial automation and intelligent collaboration, is redefining what efficiency and productivity mean in the modern world.
Introduction — The Age of Automation Has Arrived
The journey toward automation began long before artificial intelligence or digital analytics. Yet, never before has the world witnessed such rapid advancement in automation technologies as today. Businesses across manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and even creative industries are leveraging robotics in workplace environments to streamline processes, reduce risks, and optimize outcomes.
At the heart of this transformation is the rise of smart systems capable of learning, adapting, and working alongside humans. With sensors, algorithms, and machine learning, today’s robots are far more than mechanical tools—they are collaborators capable of sharing tasks and improving decision-making. This shift marks the beginning of a new era of industrial automation where efficiency and innovation go hand in hand.
A Brief History of Robotics and Workplace Evolution
From Factory Lines to Smart Workspaces
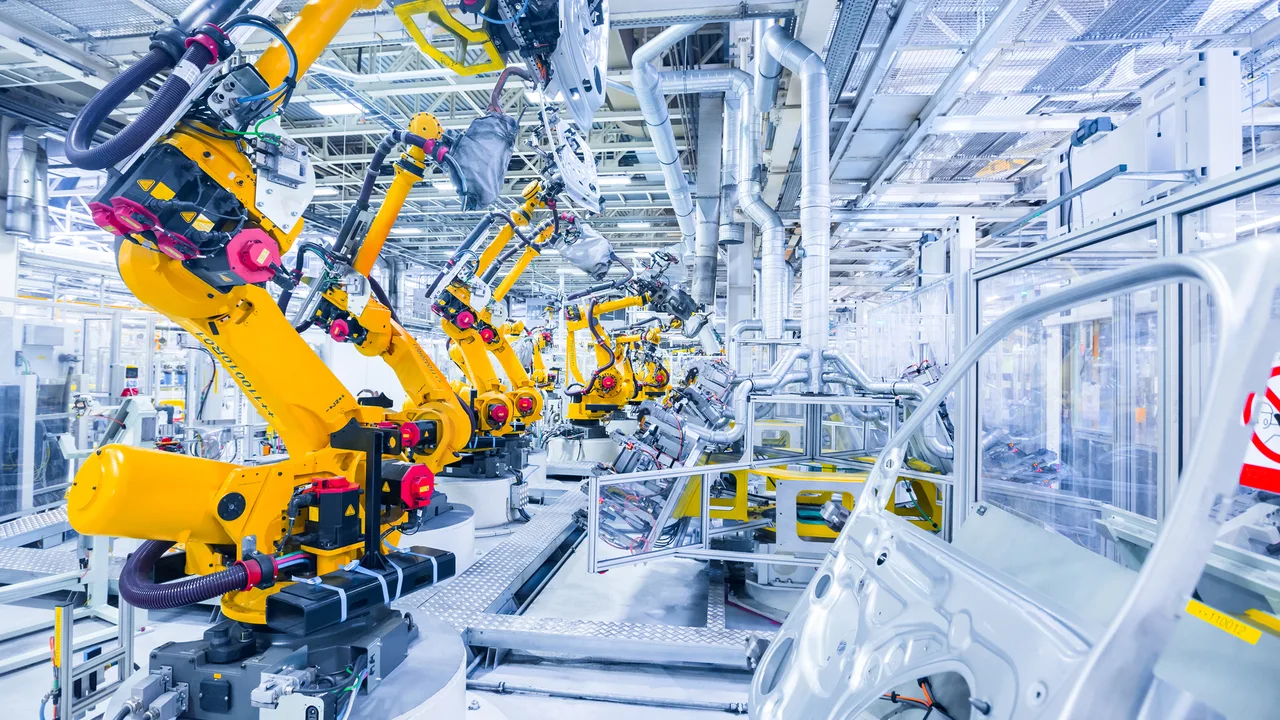
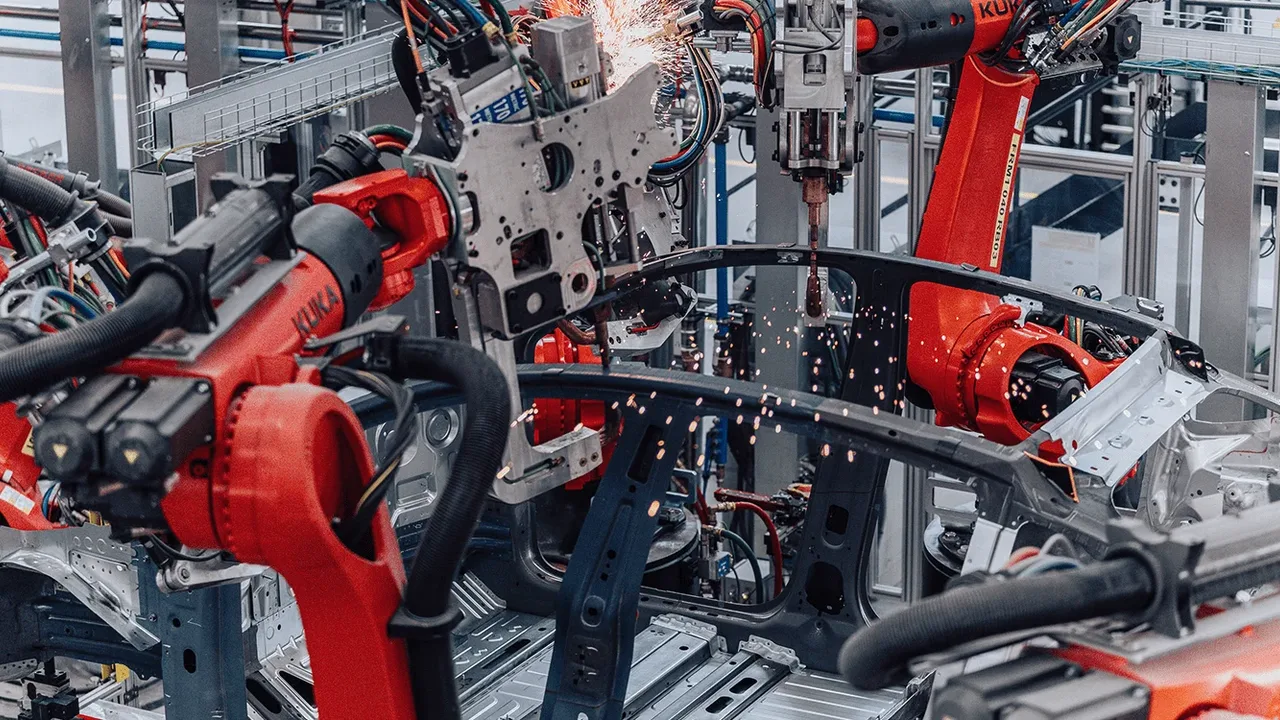
In the 1960s, the first industrial robots revolutionized automotive assembly lines. These mechanical arms could perform repetitive tasks like welding and painting with unmatched consistency. Over the following decades, advances in control systems, sensors, and computing power expanded robotics beyond heavy industry. Today, we see autonomous systems operating in sectors ranging from logistics to healthcare, proving how far automation has evolved.
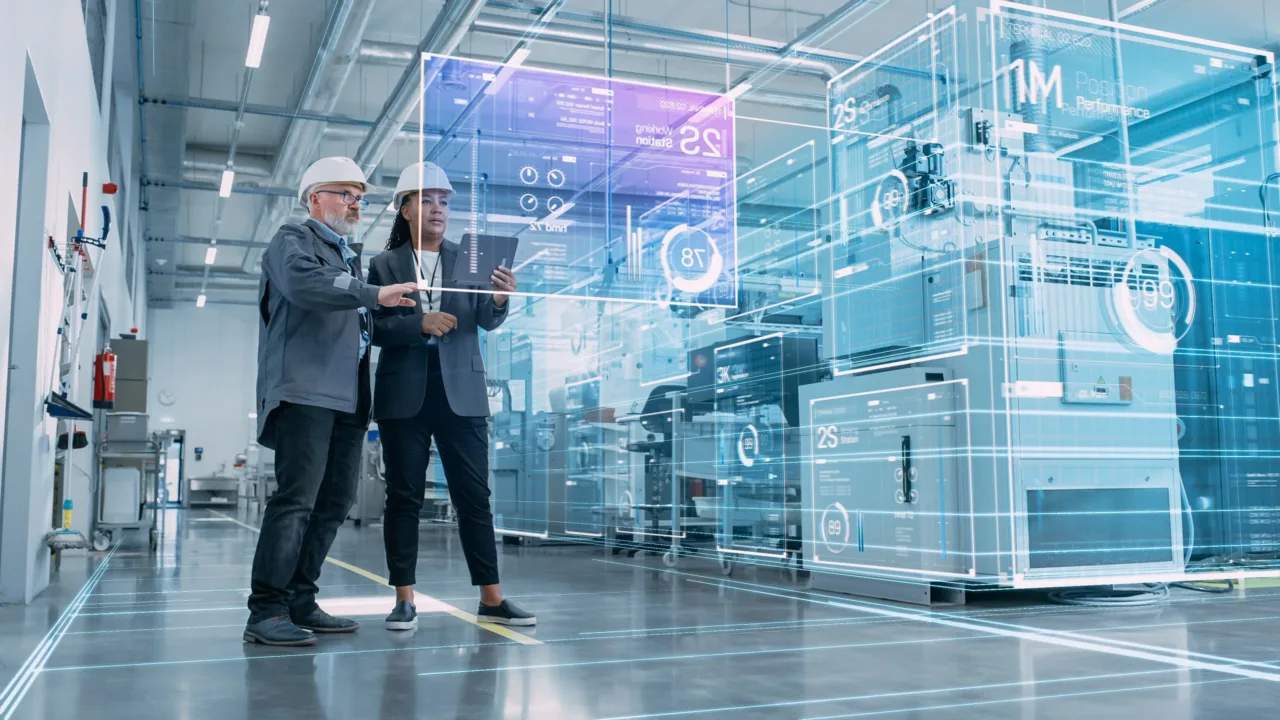
Modern workplaces are increasingly data-driven. Machines now communicate with each other and respond dynamically to real-time conditions. This interconnected network of sensors and robots, often referred to as smart manufacturing, forms the backbone of Industry 4.0, where human intelligence and machine capability converge to maximize efficiency.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution and AI Integration
The ongoing fourth industrial revolution is characterized by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological technologies. Artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) are the drivers of this change. Robots today can interpret data, recognize objects, and make decisions without direct human intervention. They no longer require strict programming; instead, they learn from patterns, simulations, and experience.
In this new paradigm, AI-enabled robots adapt to complex environments, paving the way for flexible and intelligent production systems. From predictive maintenance in factories to autonomous logistics in warehouses, the integration of industrial automation with AI has reshaped the DNA of modern industries.
The Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
What Makes Cobots Different
Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” represent one of the most significant advancements in automation. Unlike traditional industrial robots that are isolated behind safety barriers, cobots are designed to work directly alongside humans. They are equipped with safety sensors, force limiters, and intelligent path-planning systems that allow them to interact safely with workers in shared environments.
Cobots are versatile. They can assist with small-batch assembly, handle precision packaging, or manage inspection tasks that require a human touch. In small and medium enterprises, where full automation was once financially unfeasible, cobots now make advanced technology accessible. Their ease of programming and mobility allow businesses to deploy automation quickly without major infrastructure changes.
Benefits of Human–Robot Collaboration
The partnership between humans and robots has shifted from competition to cooperation. Cobots are not replacing workers—they’re complementing them. By handling repetitive or hazardous tasks, cobots allow humans to focus on creative problem-solving, innovation, and quality control. The result is higher productivity, reduced downtime, and a safer workplace.
- Efficiency: Cobots improve output rates by maintaining consistent performance 24/7.
- Safety: Human injuries are reduced as robots handle heavy or dangerous workloads.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily reprogram cobots for new tasks as demands shift.
Companies that adopt this hybrid approach—blending human adaptability with robotic precision—are achieving faster turnaround times and better product quality than ever before.
Robotics in Workplace Transformation
Automating Repetitive and High-Risk Tasks
In industries such as logistics, automotive, and pharmaceuticals, automation is revolutionizing daily operations. Robots perform high-risk tasks, from moving heavy cargo to handling hazardous materials, without fatigue or error. These machines ensure operational safety while maintaining precision at every step. The concept of robotics in workplace settings goes beyond convenience—it’s about creating safer environments where human workers can thrive without physical strain.
For example, robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors can operate inside high-temperature zones or manage chemical handling processes that pose significant risks to humans. This human–machine synergy allows companies to prioritize safety without sacrificing efficiency.
Enhancing Productivity and Precision
Every modern company faces pressure to deliver faster, cheaper, and with fewer mistakes. Robotics provides a clear path toward these goals. AI-powered machine vision systems identify imperfections, while robotic welders and cutters maintain micrometer-level accuracy. Integrating automation into workflow management software allows for seamless scheduling, resource allocation, and quality control.
In practice, these advancements lead to measurable gains in productivity. Studies show that factories implementing full-scale industrial automation can reduce production time by up to 30% while maintaining top-tier consistency. This progress exemplifies how robotics and data integration can redefine performance benchmarks in nearly every industry.
Human Adaptation and New Skill Requirements
Shifting Roles in the Age of Automation
While robots handle repetitive tasks, humans are stepping into roles that require oversight, programming, and optimization. The introduction of robotics in workplace ecosystems has created demand for new job categories—robotics technicians, data analysts, automation engineers, and AI supervisors. This evolution is transforming how workers interact with technology, emphasizing continuous learning and adaptability as essential career skills.
Educational institutions and training centers are also responding, developing programs that bridge technical and soft skills. These efforts prepare future professionals to thrive in a hybrid workforce where technology amplifies, rather than replaces, human potential.

Emotional Intelligence and Human Strengths
Even with the rise of smart automation, certain human abilities remain irreplaceable. Empathy, creativity, and complex decision-making are qualities that machines cannot replicate. In fact, the integration of robotics in workplace systems often highlights the value of these human strengths. As robots handle precision and repetition, humans focus on innovation, customer interaction, and problem-solving. This balance is what defines the next era of work—machines for efficiency, people for meaning.
Leaders are now emphasizing emotional intelligence as a key workplace skill. A successful modern employee must understand not only how to work with technology but also how to collaborate with diverse human teams in technology-driven environments. Emotional adaptability is just as critical as technical literacy.
Challenges in Adopting Robotics
Cost, Integration, and Resistance to Change
Despite the clear advantages, not all organizations find it easy to integrate robotics. The upfront investment in equipment, software, and training can be substantial. Smaller enterprises often struggle with scaling automation or adapting it to existing workflows. Additionally, there is a psychological barrier—fear of job loss. Some workers view industrial automation as a threat rather than a tool for empowerment, which can slow down digital transformation initiatives.
Successful implementation therefore depends on change management. Companies must communicate transparently about the benefits of automation, such as improved safety, upskilling opportunities, and job creation in new technical fields. Education and inclusion are crucial to overcoming this resistance and achieving long-term acceptance.
Ethical and Social Implications
The global rise of collaborative robots and AI introduces complex ethical questions. How do we ensure fair treatment for workers whose jobs are transformed? How can we avoid algorithmic bias in recruitment or production monitoring? These questions are shaping new labor policies and ethical frameworks around automation. Researchers and governments are working to establish regulations that promote safe and equitable implementation of technology in the workforce.
At the same time, the debate over the digital divide continues. Not every country or community has equal access to modern technology. Ensuring that robotics in workplace innovation benefits everyone—rather than widening inequality—will be a major challenge in the coming decade.
Real-World Examples of Robotics in Workplace
Manufacturing and Warehousing
Few sectors demonstrate the impact of robotics as vividly as manufacturing and logistics. Automated guided vehicles navigate massive warehouses with minimal human oversight, while precision robotic arms assemble products at lightning speed. Companies like automotive giants and e-commerce leaders use autonomous robots to move packages, load trucks, and manage inventory around the clock.
These systems demonstrate how industrial automation and data analytics combine to optimize efficiency. In some factories, cobots and humans work side by side, adjusting production in real time to meet demand. The result is a more flexible, resilient supply chain capable of adapting to market fluctuations instantly.
Healthcare and Service Sector
The influence of robotics extends far beyond industry. In hospitals, surgical robots assist doctors with precision beyond the human hand. In hotels and airports, service robots provide customer support, reducing waiting times and improving user experience. The integration of robotics in workplace models within service industries shows how automation can enhance—not replace—human care and attention.
The Future of Human–Robot Collaboration
Next-Generation Technologies
The next wave of innovation will make robots more perceptive, autonomous, and intuitive. Machine learning algorithms are allowing robots to learn from human gestures, tone, and behavior. Predictive maintenance powered by AI minimizes downtime, while cloud-based robotics allows real-time control from anywhere in the world. Future cobots may even possess self-learning capabilities, improving their performance without explicit reprogramming.
- Adaptive robotics: Machines that learn and adjust to user behavior.
- AI integration: Smarter systems that interpret context and make real-time decisions.
- Voice and gesture control: Allowing intuitive communication between humans and machines.
This transition moves the focus from automation—doing tasks automatically—to augmentation, where robots enhance human ability and creativity. Workplaces will no longer be defined by repetitive output but by human–machine synergy.
Vision for 2035 — A Symbiotic Workplace
By 2035, experts predict that robots and humans will collaborate seamlessly in most industries. AI-driven scheduling will align team workflows, robotic exoskeletons will prevent workplace injuries, and intelligent analytics will guide decision-making. In this symbiotic environment, people will supervise, innovate, and strategize while machines handle precision execution.
The future workplace will not be about replacing human effort but amplifying it. As technology continues to evolve, success will depend on how effectively organizations integrate automation without losing the essence of human creativity and purpose.
Building a Smarter, Safer, and More Inclusive Workplace
The rise of robotics in workplace is more than a technological revolution—it’s a cultural and social transformation. As automation becomes a standard part of daily operations, businesses must embrace adaptability, continuous learning, and responsible innovation. The goal is not just efficiency, but empowerment: enabling humans to focus on what they do best while machines take care of the rest.
Ultimately, the future of work is not about humans versus robots—it’s about collaboration. Organizations that understand this will lead the next wave of innovation, creating work environments that are safer, smarter, and more inclusive for all.